Why schema markup matters for B2B
Discover how schema markup can drive visibility and trust for B2B and enterprise websites. Learn use cases, implementation tips, and SEO best practices.
Nearly 73% of pages on the first page of Google use schema. Structured data for B2B websites could be the difference between your page showing up as one of those little blue links—or if you’re really lucky, as a SERP feature—or not at all.
As a B2B company with complex sales cycles and research-driven customers, you’re not like a short-cycle B2C organization. You need strong schema to get good click-through rates and organic visibility.
But what exactly is schema markup for B2B marketers—and why should you care?
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is code you add to a page’s HTML. While not visible to your site’s users, schema makes it easier for search engines to understand your website content and better represent it in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
This guide will walk you through:
- B2B and enterprise SEO’s unique needs
- How B2B schema builds EEAT and visibility
- Schema’s influence on AI search results
- High-impact schema recommendations for B2B marketers
- How to scale schema for enterprise sites
- Structured data for the Knowledge Graph
- Tracking, testing, and measuring schema impact
- Common mistakes
- Best types of schema to get started with
Understanding the unique needs of B2B/enterprise SEO
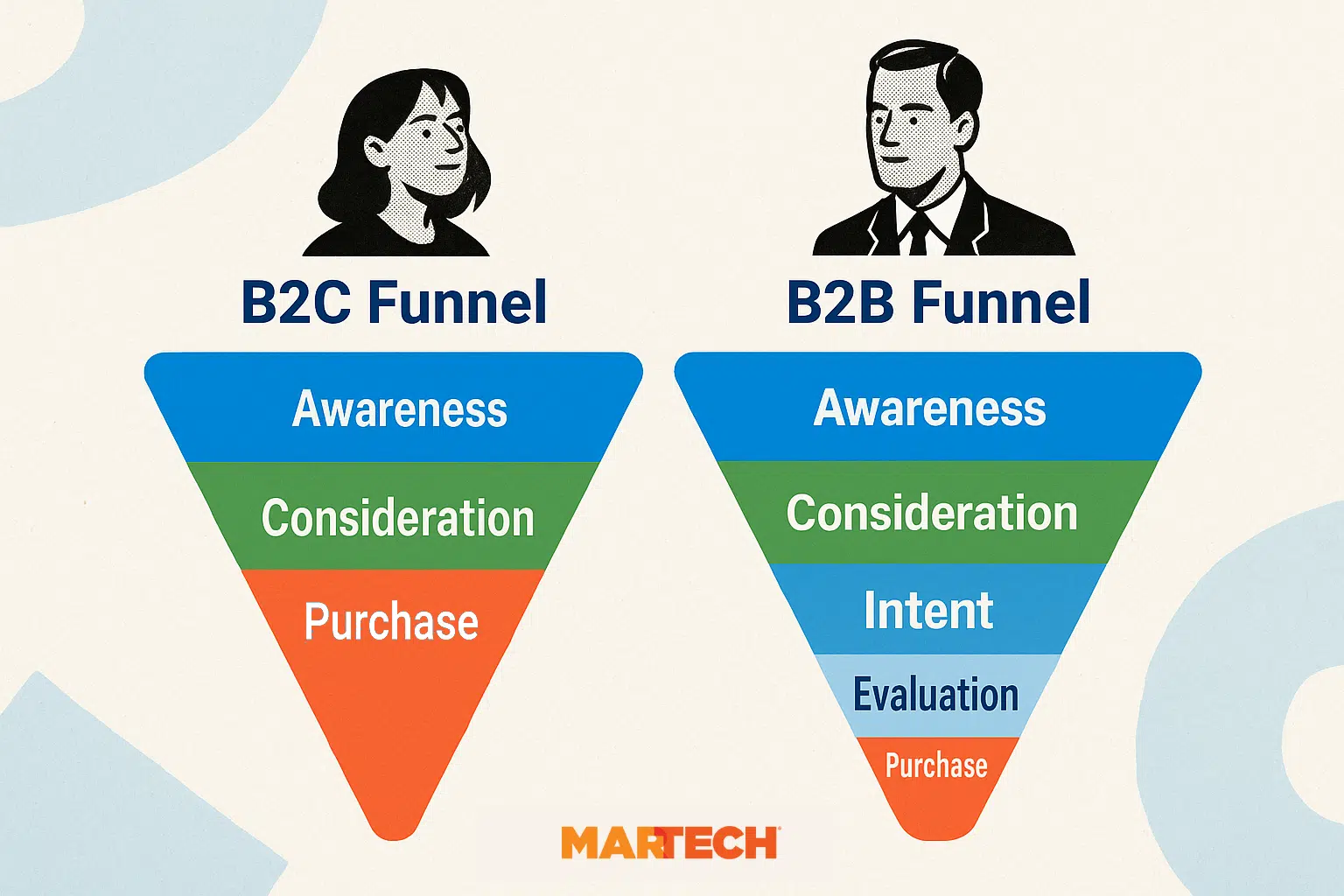
B2B stands out compared to B2C because of its much longer marketing journey.
B2B buying periods take months, not minutes. Multiple stakeholders involved and higher costs mean decisions to buy take time.
Due to the extended timeline, top- and middle-funnel content needs to do a lot of heavy lifting. You need B2B technical SEO to optimize each of these pages, especially those in pre-contact stages, otherwise you’re missing out on valuable organic traffic.
This all means that as a B2B company, you’re often looking at a much larger website and a more complicated buyer’s journey. Schema for enterprise content brings order to that complexity, making it easier for search engines to understand each page’s purpose and surface them at the right time in the buyer’s journey.
Enterprise SEO for B2B companies faces unique challenges. Where B2C focuses on quick conversions, B2B technical SEO has to support an enterprise, often months-long, research process.
This is why schema for enterprise content is so essential. Multiple decision makers will need to find and review all sorts of information like webinars, whitepages, articles, and podcasts before making a final purchase decision.
How B2B schema builds EEAT & visibility

Expanding on your EEAT (expertise, experience, authority, and trust) signals is key to turning visitors into buyers.
Google’s EEAT guidelines are crucial for B2B websites operating in specialized fields or offering high-cost, enterprise solutions. The stronger your EEAT, the more people will trust your company’s authority.
B2B schema makes it possible for you to explain in detail what your business is, what you’re trying to accomplish, and any additional experience you have.
How can schema possibly help you so much?
B2B users want to read all of your content. It’s critical to their decision-making: case studies, whitepapers, product descriptions, FAQs, and more.
All pages will need their own optimized schema to maximize the visibility of each stage of the funnel.
Schema markup helps your content appear at critical research touchpoints throughout the sales funnel. It positions you as the authority in your field so prospects will seek your opinion.
Whether you want to highlight your case studies or improve organic visibility for your webinars, schema provides the much-needed edge for appearing in the complex B2B sales cycle.
In a crowded B2B space, schema makes your product or service stand out. It enables your solution to appear in reviews, featured snippets, and AI Overviews.
Unlike B2C transactions—often driven by impulse and short buying cycles—B2B purchases are high-consideration decisions that require trust, relationship-building, and sustained engagement. Meeting the informational needs of diverse stakeholders through strategic content is essential, contributing to a longer, more complex conversion funnel. Search visibility gets you in front of those customers so you can meet their needs.
The added visibility schema provides for that extra content? That makes all the difference.
A B2B SaaS website selling a specific product would use product schema on that product landing page. Use this schema to include things like your average star rating and number of ratings for that product. Google can more readily parse and understand the information on your page and surface it to relevant search queries.
And yes, schema can make a huge difference for your site. One company reported a 400% increase in organic traffic after optimizing more than 4,000,000 pages over seven websites.
Schema can be used to relay information about anything to search engines, including products, services, events, and even organization structure. The full library of objects with schema markup can be found at Schema.org.
Capturing a featured snippet or appearing in the AI Overview or People Also Ask box in the SERPs means higher click-through rates to your website. And increased authority. It’s a win/win.
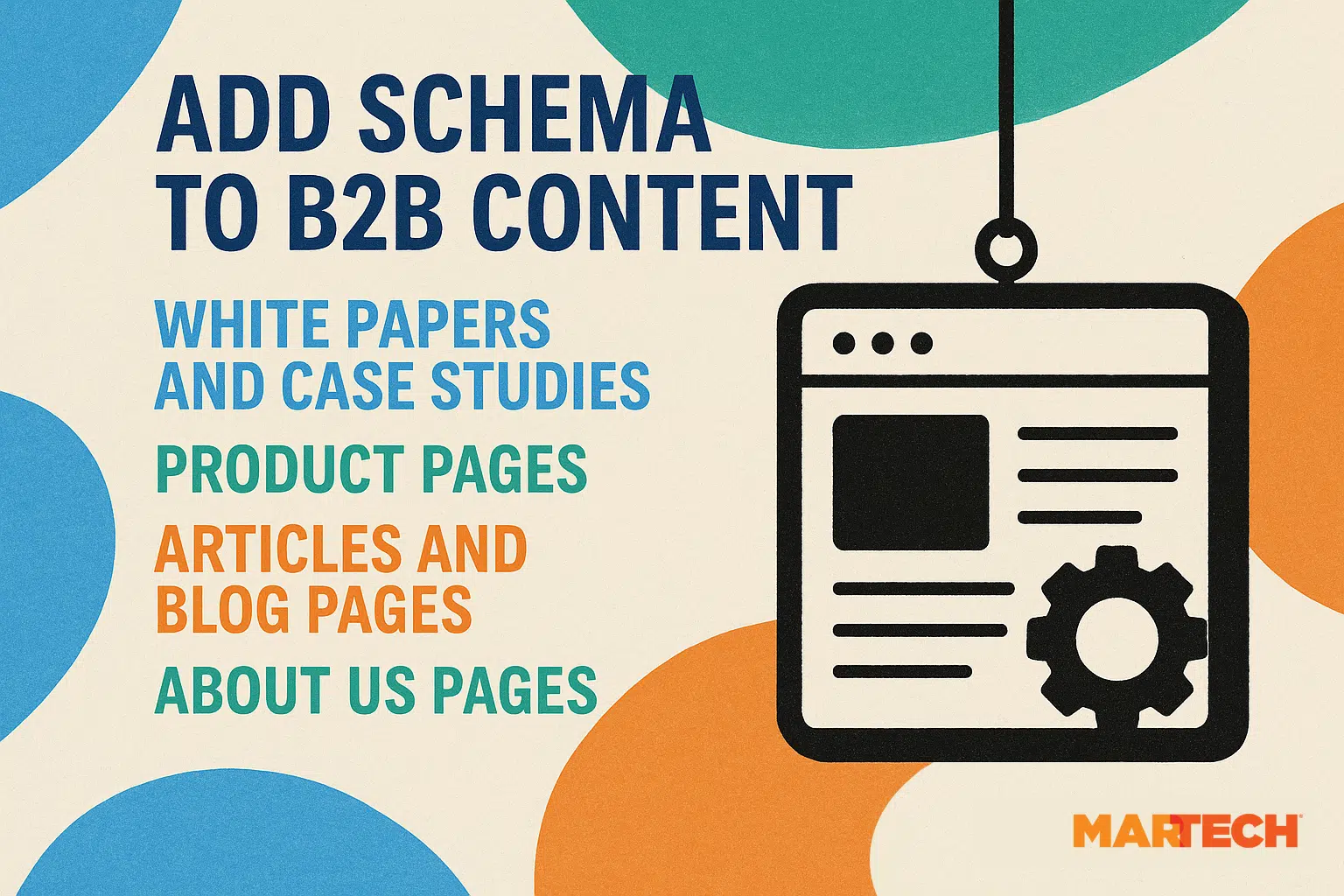
Here are a few enterprise SEO structured data use cases:
- White papers and case studies benefit by adding more information to your authors and improving EEAT signals.
- Product pages benefit by adding product schema that includes star ratings, product features, and customer testimonials.
- Articles and blog pages benefit by adding article and FAQ schema to improve the chances of appearing in SERP features.
- About us pages benefit by adding organization schema to improve EEAT signaling.
Implementation tip: For case studies, emphasize the “author” property in the schema code by including industry-relevant credentials and experience. Case studies written by visible experts are more likely to rank.
The only problem with schema for enterprise content?
Deployment.
“Enterprise B2B schema deployment”—has a phrase ever filled you with more dread?
We’ve got insider knowledge here: There’s a certain approach to enterprise B2B schema deployment that makes the process much smoother.
For one, you’ll want to use templates and automation tools like Schema App or Google Tag Manager and a good project management system to keep things consistent sitewide.
But we’ll get into the nitty-gritty details of this in a bit.
Schema’s influence on AI search results
B2B schema is a heavy hitter when it comes to LLM-powered search.
Take AI Overviews, for example.
When Google generates an AI Overview, it wants to pull data from a source that is both authoritative and easily accessible.
What does this mean with regard to B2B schema?
Well, Google hasn’t officially confirmed that schema is a direct factor in AI Overviews. But we all know that structured data makes your content more machine-readable, which improves your odds of inclusion.
For B2B sites, this means your white papers, case studies, and product pages are much more likely to appear in AI Overviews—and even for other LLM-powered search tools, like ChatGPT.
Any structured data that helps AI understand your content also makes it easier for your brand to appear in Google’s Knowledge Graph—that information box that appears to the right of the search for branded queries.
That information you see up there on the right? Think of that as Google’s cheat sheet on your company.
You can make it even easier for Google to learn more by properly implementing the right B2B schema—though Knowledge Graph visibility isn’t just fueled by structured data. It’s also influenced by authoritative third-party resources like Wikidata and Crunchbase. It’s these sources and your structured data plan that create your digital footprint and reinforce your brand authority.
We’ll get into more on how you strategies to improve your Knowledge Graph presence in a bit.
High-impact schema types for B2B marketers
Browse Schema.org and review the types of structured data available to find what aligns best with your site.
Let’s take a closer look at some high-impact types of schema markup that can make the difference for B2B. We’ve already mentioned a few of these above, and we’ll go into more detail here:

1. Organization and product schema
Organization pages like the “About Us” or “Why Us” pages are important to show off your authority and experience in your field.
You can highlight that expertise using Organization and Corporation schema. This schema lets you link out to your other relevant social media profiles so Google can associate you with what you’re posting on LinkedIn, which is another EEAT boost.
If you have reviews or testimonials pages, you can also add Review or Rating markup to enhance your credibility.
Pro tip: Comprehensive organization schema that helps Google better understand your company leadership, structure, and industry can help sneak more information into the Knowledge Graph.
2. Article/WebPage schema
Use Article or WebPage schema for your case studies, whitepapers, articles, and blog pages.
Article schema lets you speak at length about the author. You can link to other relevant social media profiles and bylines to build the authority of the piece.
This can help strengthen your content’s connection to expertise.
Case studies with structured data showcase business outcomes in a form that search engines can easily surface. That means you can put material critical to the research stage in front of B2B decision-makers.
3. Product schema
Product schema, as already mentioned, makes it easier to explain what your product offering is and previous user’s experience with it. It can cause information like star ratings, product images, price, number of reviews, brand, and shipping details to appear in the SERPs. And it makes it easier for your products to appear in rich snippets, Google shopping free listing, and product carousels.
4. Event markup
Use Event markup to highlight relevant dates, times, locations, and registration details for your webinars or conferences. This increases your chances of appearing in Google’s events carousel and in front of potential attendees.
5. Job postings
JobPosting schema makes it easier for Google to pull details from your listing and add them to dedicated job pages or Google’s own job listings dashboard.
6. Service schema
Believe it or not, service schema is often overlooked.
Service schema clarifies what services you’re offering and where. It’s especially valuable for enterprise B2B companies offering more complex professional services that can’t be easily classified as products.
For example, a B2B consulting firm can mark up details like project scope, price, and benefits, making that information more likely to be displayed in a featured snippet or a Local Map Pack.
7. Miscellaneous markup
Use FAQPage, HowTo, and TechArticle schema for content like API documentation, troubleshooting guides, or integration tutorials. This markup positions your site as the authority for tech buyers.
FAQPage is especially useful in helping pages appear in People Also Ask boxes and FAQ rich results (that collapsable Q&A section that sometimes appears directly beneath your search listing).
Combine TechArticle schema with HowTo schema for implementation guides to signal the authoritative and technical nature of developer-centric content.
This approach means your technical content is more likely to appear for developer-focused searches, positioning your company as the technical solution and strengthening trust signals for B2B buyers.
How to scale schema for large B2B sites in 6 steps
Enterprise sites often have thousands of pages in need of schema markup.
But here’s the problem: implementing that much schema manually is next to impossible.
The solution?
Automation through enterprise SEO tools like data feeds, structured data templates, and schema translators. And, of course, be mentally prepared to undertake a lot of quality assurance (QA) checks.

Now, let’s dive into how you can push schema markup at scale live across your entire enterprise site.
Step 1: Make sure you have the right tools
Enterprise SEO tools you should be using:
- Google Tag Manager
- Data feed of choice (Google Merchant feed, HubSpot blog feed, etc.)
- Schema App
- Content management system (CMS) plugins (like Yoast SEO for WordPress)
- Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator
Before you start pushing the schema on your enterprise site live, you’ll want to establish a schema governance framework.
Step 2: Establish a schema governance framework
A schema governance framework is how you’ll keep your launch process streamlined and replicable. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Required vs. optional properties for each schema type
- Approval workflows for schema updates
- Naming conventions to maintain consistency across all properties
- Implementation documentation to standardize workflows
- List of stakeholders required to approve the schema process
Typically, a technical SEO specialist handles oversight for this kind of project. The specialist then handles communications between the marketing and development teams to maintain consistency and quality.
Even with a governance framework established, you’re still not quite ready for a launch plan. Instead, take a look at what CMS your site is operating on.
Step 3: Review your site’s CMS

How you implement schema across an enterprise site depends on your content management system:
- WordPress: Enterprise sites are usually too large to use basic plugins like Yoast. Instead, you’ll want to use Advanced Custom Fields. This will create structured content that automatically outputs the correct schema.
- Sitecore: Use xDB to connect your customer data with schema implementation. This provides a much more personalized service or product page experience.
- Adobe Experience Manager: Similar to WordPress, use a tool called Component Content Architecture to create schema templates. These will be automatically applied to content fragments.
- Custom CMS: You’ll need to work with a developer to create schema generation rules. Base things on page templates or content types to make the process faster.
Step 4: Create a launch plan
After all of that, it’s finally time for the launch plan. Here’s what you should do to ensure a timely and accurate process:
- Determine what data feeds you can use as a source for your schema markup (e.g., Google Merchant feed, HubSpot blog feed).
- Identify the pages that would most benefit from schema (articles, service pages, events pages).
- Choose a schema translator like Schema App. This will help you map data from your source feed to the correct schema properties.
- Configure your translator. For example, you can configure Google Merchant feed data to map product attributes into the product schema type.
- Implement your schema markup. Use the JSON-LD code generated by the schema translator using Tag Manager or another CMS plugin.
- Test and validate your schema markup. Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator are your friends for making sure everything has been properly set up.
What’s next after you finish pushing everything live?
Unfortunately, it’s not yet time to celebrate. Once you’re done with launching schema markup at scale for your enterprise B2B site, it’s time to QA.
Step 5: QA schema at scale
Always include quality assurance in your implementation plan. When it comes to enterprise sites, it’s almost impossible not to make a mistake.
Here’s how you can QA your new enterprise schema:
- Automate weekly Screaming Frog crawls with custom extractions to identify any schema inconsistencies
- Schedule regular Google Search Console audits to review for structured data errors
- Integrate your process with CI/CD pipelines so schema is validated during deployment
Get comfortable with auditing. You’re going to need to do it on a regular basis to make sure nothing breaks when your back is turned.
Maintain open communications with your dev team throughout this process. Make sure to educate them so they understand why you’re blowing up their queue.
Step 6: Maintaining and updating schema markup at scale
The job isn’t done, even after you’ve pushed everything live. You’ll need to continually monitor and update schema as products change and new data is added.
Keeping everything accurate means building a clear ownership plan to understand who can control what. Establishing a central schema governance team means maintaining quality schema across your enterprise B2B site.
Don’t forget to check how your schema markup influences your Knowledge Graph visibility.
When it comes to B2B enterprises, appearing in Google’s Knowledge Graph isn’t just a vanity check. It’s a matter of managing your digital reputation at scale.
Visibility in Google’s Knowledge graph means gaining advantages like:
- Immediate brand recognition in the SERP
- Stronger trust signals
- Better visibility for company information like leadership, location, and founding date
- Stronger positioning against competitors
A strong B2B schema markup strategy makes a big difference when building out a Knowledge Graph foundation, but it shouldn’t be the only thing on your list.
Here’s what your strategy should include:
- Organization schema: Make sure to include all relevant properties like foundingDate, location, parentOrganization, and reward information
- Wikidata presence: Creating or optimizing your Wikidata entry is key for larger enterprises since Wikidata is such an influential source for the Knowledge Graph
- Crunchbase presence: Update your Crunchbase profile, especially if you’re a technology company and/or startup
- Consistent NAP info: Keep your Name, Address, and Phone Number consistent across all digital properties—now is not the time to confuse Google
And yes, this is a lot of work, and yes, it is worth it. Pages with schema get 40% higher click-through rates than pages without. Establishing an enterprise B2B schema strategy means improving your visibility and building your authority, a win/win across the board for SEO.
Tracking, testing, and measuring impact
Now that you’ve taken the time to create and implement B2B schema, let’s take a look at how to monitor structured data impact and measure return on investment (ROI).
Google Search Console is the best way to track schema markup performance. Use it to monitor impressions, clicks, and, most importantly, any errors you need to fix. You can find errors in Google Search Console on the rich results reports. Most schema issues will be found under the “Enhancements” section. Errors involving product and merchant listings can be found under the “Shopping” section.
Test things regularly with Google’s Rich Results tools and Schema Markup validator so you can be certain your code is error-free.

Beyond Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema Markup validator, enterprise B2B teams should implement automated monitoring. Try using a tool like Screaming Frog to pull schema during crawls to make regular quality checks across thousands of URLs.
Enterprise B2B sites should continuously improve schema with A/B testing. Try testing different approaches to your structured data markup like:
- Varying what features you include for solution page product schema
- Trying new formats for FAQPage schema for technical content
- Adjusting HowTo schema to see what gets stronger featured snippet results
When it comes to measuring the impact of B2B schema, go above and beyond the typical key performance indicators (KPIs) of conversion rates, impressions, and clicks. Things are different for a B2B site. And even more so for an enterprise B2B site.
Here’s the schema-specific KPIs you should be tracking in addition to those metrics just mentioned:
- Changes in organic click-through rate (CTR) for pages with schema vs. pages without schema
- Appearance in rich results and SERP features for high-value keywords
- Knowledge panel completeness score (review how many fields have been populated)
- Rich results impression-share compared to competitors
The most important KPIs you track can be tied to leadership’s goals:
- Service pages: Track visibility in featured snippets and AI Overviews for these pages. Tie that increased visibility to increased lead generation from those pages.
- Organization pages: Monitor brand search volume and knowledge panel visibility. Tie this to increased visibility across LLM-powered search like ChatGPT, which loves to have more information about your brand.
- Event pages: Measure registration rates and attendance. Compare those numbers with organic visibility before and after schema implementation.
And you don’t need to track this data by hand. You can use tools like Semrush’s rank tracking to automate these processes so leadership reports are a matter of exporting already-made graphs.
Common B2B enterprise schema mistakes
Even after you use a structured data testing tool to confirm that your schema markup is rendering properly, you could still face errors.
It’s easy to make mistakes when it comes to schema, especially if you’re working at an enterprise scale. Beware these common mistakes:
Inconsistent data
One common mistake with B2B schema is inconsistent property values.
Property values are used in most forms of schema. These values provide key details, such as name, address, and other important information to Google.
Inconsistency means confusion for the search engines.
That makes it harder for your page to rank.
Avoid this by pulling your data from a single source of truth.
Missing recommended properties
Every schema type has required and recommended properties. Most B2B sites will hit the required properties but miss the recommended ones.
Article schema, for example, does not require you to include author, datePublished, headline, or dateModified properties. But all of these pieces of information make a huge difference when it comes to EEAT.
Schema that contradicts on-page content
This is especially prevalent in dynamic B2B sites that frequently update service offerings, event dates, and product features. Make sure to always update your schema after you update your content.
Product pages also frequently suffer from this problem. If you put a product on sale or update the pricing, make sure the number listed on the page reflects the number listed in the schema.
Start with these three schema types today

No need to rush into the B2B enterprise schema plan. We know that’s a serious commitment, and you’ll want to do your due diligence to be consistent and accurate across the organization.
But you can still start to use schema markup today, or enhance how you implement schema markup. Every bit counts towards pushing your momentum in the right direction for organic search. Just start small with these high-impact options, and you’ll be on your way:
- Organization schema on your “About Us” page to build EEAT signals (use the sameAs function to link to your relevant social media accounts)
- Product schema (or service schema) on your highest performing offer pages
- Article schema (make sure to include any and all relevant information about the author) on your blog pages