How to vet AI tools for marketing: Key questions to ask
Before buying any AI tool, ask the right questions. Learn how to vet AI solutions for fit, ROI, data privacy, and integration across your marketing stack.
When you’re vetting AI tools for marketing, asking the right questions can help you find the right solutions for your organization. It can also help you avoid tools that aren’t worth the hype (or the money).
Imagine investing thousands of dollars into an AI platform only to realize its surface-level features don’t make an impact. Or worse: It creates quality, compliance, or security issues.
It’s a scary thought. Yet as the technology evolves quickly, it can be difficult for decision-makers to know what criteria matters most when buying.
In this article, we’ll discuss the questions you should ask when selecting AI marketing tools to find a solution worth the investment.
What problem does this tool solve?
The first step in evaluating an AI tool is to get clarity around what problem it actually solves.
Some tools offer high-level solutions that can address critical pain points or bottlenecks in your marketing operations. For example, if your team relies on high-volume email marketing, Brevo’s AI writing assistant can help you create and test diverse subject lines quickly to see what works. This could help your team scale output and optimization efforts for better long-term performance.
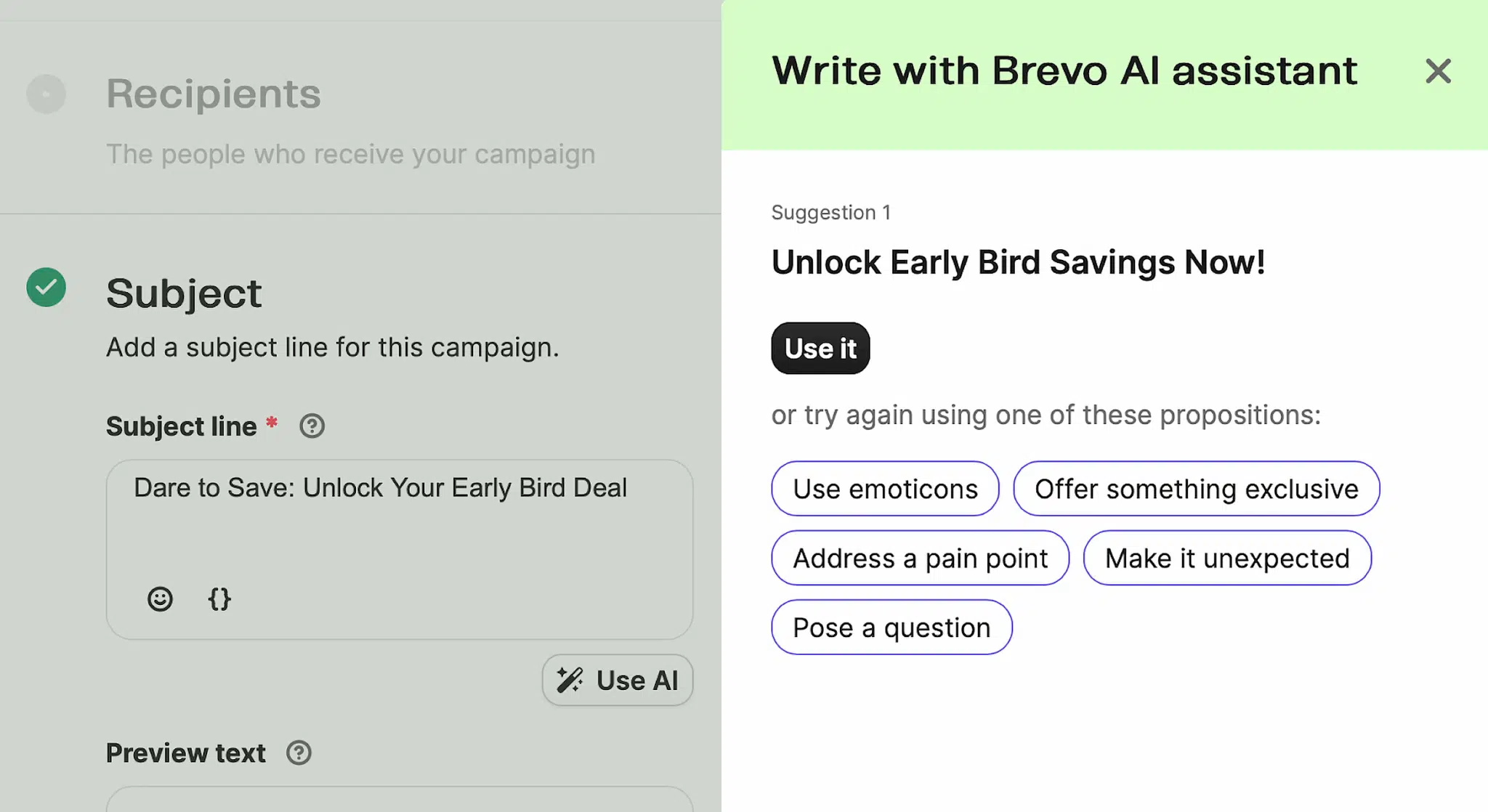
Others might have flashy features that look good on paper but don’t actually move the needle. For example, a social media management platform might have an AI feature that generates image captions. This could streamline post production but wouldn’t be helpful if the true pain point is generating post ideas—not the content itself.
Further reading: Getting more done with AI
How to choose AI tools that solve real problems
Review your marketing operations closely, and get input from key team members like marketing leaders and even end users. This means conducting interviews or surveys with your marketing team to understand their daily challenges.
For example, ask content creators how long it takes them to write email campaigns from scratch. Or, find out from campaign managers which steps in their workflow require the most back-and-forth revisions.
You might discover that your team spends hours manually segmenting audiences, struggles with A/B testing setup, or frequently gets bottlenecked waiting for design approvals.
Look for friction points that slow down campaign creation, reduce conversion rates, or require too much manual effort.
Let’s say your team notices a drop-off in site engagement and high bounce rates on relatively high-intent pages.
An AI-powered chatbot could be a solid solution. It can proactively ask customers if they have questions, recommend resources, or connect them to a sales rep. This can boost lead generation and reduce drop-offs without requiring significant time and resources
Is this tool AI-native or AI-wrapped?
Right now, it feels like every tool on the market is promising AI-driven features. Keep in mind that a marketing tool with AI features isn’t the same as an AI-native tool.
AI-native tools are built from the ground up with machine learning and artificial intelligence at their core—not as an afterthought. These are tools like Jasper, Claude, and Perplexity.
This means that the AI functions are central to the platform. They may be capable of more advanced automated decision-making, content generation, or predictive analytics.
AI-wrapped tools overlay AI capabilities onto existing software. They may use third-party integrations, like ChatGPT, to offer AI features. These features may be relatively small, like a subject line generator for an email tool or automatically generated meeting transcripts from a video conferencing tool.
AI-wrapped tools can offer convenient solutions for existing users. However, they might lack the deep integration and more sophisticated capabilities of purpose-built AI native solutions. They may not have advanced brand guardrail features, for example. These features can impact output quality significantly.
Why AI-native tools may have the advantage
AI-native tools typically offer better performance, more sophisticated features, and greater scalability as your needs evolve.
They’re also more likely to maintain competitive advantages as the AI landscape rapidly changes. AI-native tools can quickly adopt new features when breakthroughs happen because they’re built entirely around AI from the start. They don’t have code or systems that may have technical limitations or incompatibility with new AI features.
Jasper, for example, is an AI engine that was designed for marketers.
It offers features like no-code AI app development, which allows marketers to create custom workflows in a few minutes. Marketers can also use the platform’s advanced image creation features to remove or replace an image’s background, remove in-image text, or even reimagine a photograph.
In addition to advanced AI content generation, the platform also has advanced options that you’ll likely only find with AI-native tools. The platform has built-in compliance standards for companies in regulated industries, for example. It also has the ability to configure context on different marketing campaigns based on audience insights and platform best practices.

When to consider AI-wrapped tools
AI-wrapped tools can still have a place in your tech stack, so you shouldn’t automatically discount them. Especially if a platform you’re already using successfully introduces new AI features that can streamline tasks or campaign management.
For example, all-in-one email marketing software MailChimp now offers AI features such as automated personalized campaigns and first draft writing.
These features can benefit teams that already use MailChimp. They may want to streamline email campaign creation, but they know their brand inside and out and don’t need advanced features like brand guardrails or compliance standards.
These AI-wrapped features help marketers draft copy, customize campaigns with branding, and include automated product recommendations in emails. Marketers can use these features to scale campaign output and personalization.
To decide whether an AI-wrapped solution offers the functionality you need, simply request a demo. This can help you assess if the AI features are useful and address your key pain points.
How does the tool fit into my current marketing stack and data flows?
It can be headache-inducing if your new AI tool doesn’t integrate seamlessly with your existing tech stack and it can create data flow issues between the two tools. This can make both adoption and ongoing usage difficult and clunky.
An AI tool may be most useful if it can connect to essential data sources and fit within your existing process. It’s less helpful when it doesn’t integrate seamlessly and complicates existing workflows.
A study from Influencer Marketing Hub found that 69.1% of marketers have integrated AI tools into their marketing processes.
However, the study also found that 69.8% of participants have encountered technical challenges when they try to use AI for their marketing efforts. These challenges could include data compatibility issues, integration difficulties, and steep learning curves.
Before selecting a tool, assess data flow and tech stack compatibility with the following questions.
Data flow compatibility
When considering AI tools for marketing, it’s important to ask whether a specific tool can seamlessly ingest data from your CRM, customer data platform, and analytics systems. And will it require manual data exports and imports, or can it access real-time data streams?
Some platforms have ready-made (or “native”) integrations or expansive API options. These integrations can help you connect essential tools in your tech stack. This helps the platforms transfer data back and forth automatically for better data flow.
For example, Claude integrates with Google Drive. This integration allows users to add specific Google documents into Claude for easy access.
Look for tools with ready-made integrations with your existing tech stack, and ask about available API capabilities. If you’ll be relying on a custom API, make sure that you have the technical and developer resources first.
Tools without native integrations may also require time-consuming manual importing and exporting processes. These processes can be prone to human error and can prevent data flow issues between tools. In some cases, this can result in disjointed data silos.
Pro tip: Don’t forget that data flow should move both ways. How will the AI-generated insights, content, or recommendations flow back into your other marketing tools? If the new solution produces valuable outputs that can’t be easily used elsewhere in your stack, its impact will likely be limited.
If you’re relying on an AI tool to create your landing pages, for example, you don’t just want an easy export of the landing pages to your site. You may also want AI to get performance data from the pages you’re creating for better optimization.
An important question to ask is whether an AI tool can enhance your existing processes or force you to rebuild them.
Some organizations may find that the best AI tools integrate naturally into their current workflows. They should make teams more efficient rather than complicating existing processes.
If a platform does require extensive revisions to your team’s processes, consider whether the ROI will be worth it. This may be the case if:
- The tool solves a major problem or bottleneck. Your current process has significant inefficiencies, manual work, or quality issues. The AI tool directly addresses these issues and can offer substantial time savings or quality improvements. For example, benchmarking brand visibility and perception has been a major challenge, but Semrush Enterprise AIO solves that.
- You were already planning changes. Your existing tools are outdated, expensive, or lacking features, or your team was already considering process improvements or system upgrades.
- The math works. Implementation costs (including training, setup, temporary productivity loss) will be recovered through efficiency gains or new performance-boosting capabilities.
Redundancy assessment
As marketing platforms constantly roll out new AI features, make sure that tools you’re assessing aren’t made redundant by your existing tech stack. It’s important to ask yourself and your team whether the tool you’re considering will duplicate capabilities you already have in other platforms.
Redundant tools increase costs unnecessarily. They can also complicate your tech stack without adding value. In some cases, they may even increase the risk of data flow issues if your tech stack bloats and there are complex integration challenges.

Let’s say your CRM has marketing automation features built into the platform. If those features are already sufficient, you don’t need to find a dedicated AI-powered automation tool. You can do this by:
- Auditing existing AI investments across departments. Map out what AI tools different teams are already using. Identify overlapping capabilities like content generation, data analysis, or automation features that each tool provides.
- Evaluating integration vs. consolidation opportunities. Determine if separate tools can share data and workflows effectively. Or, if a unified platform would eliminate duplicate subscriptions and reduce training overhead.
- Calculating the true cost of feature overlap. Factor in not just licensing fees but also the hidden costs of managing multiple vendor relationships, training staff on similar features, and potential data silos created by redundant tools.
What level of control and transparency does this tool offer?
Black-box AI tools don’t share their internal decision-making processes; they only provide output. While these tools might deliver fast results, they can introduce more risks for marketing organizations that need transparency.
ChatGPT is a black-box AI tool, for example. It will respond to prompts and deliver output based on your instructions. However, you won’t be able to see the decision-making processes it used to create that output. We don’t know what algorithms it uses or what the tool’s internal workings look like.
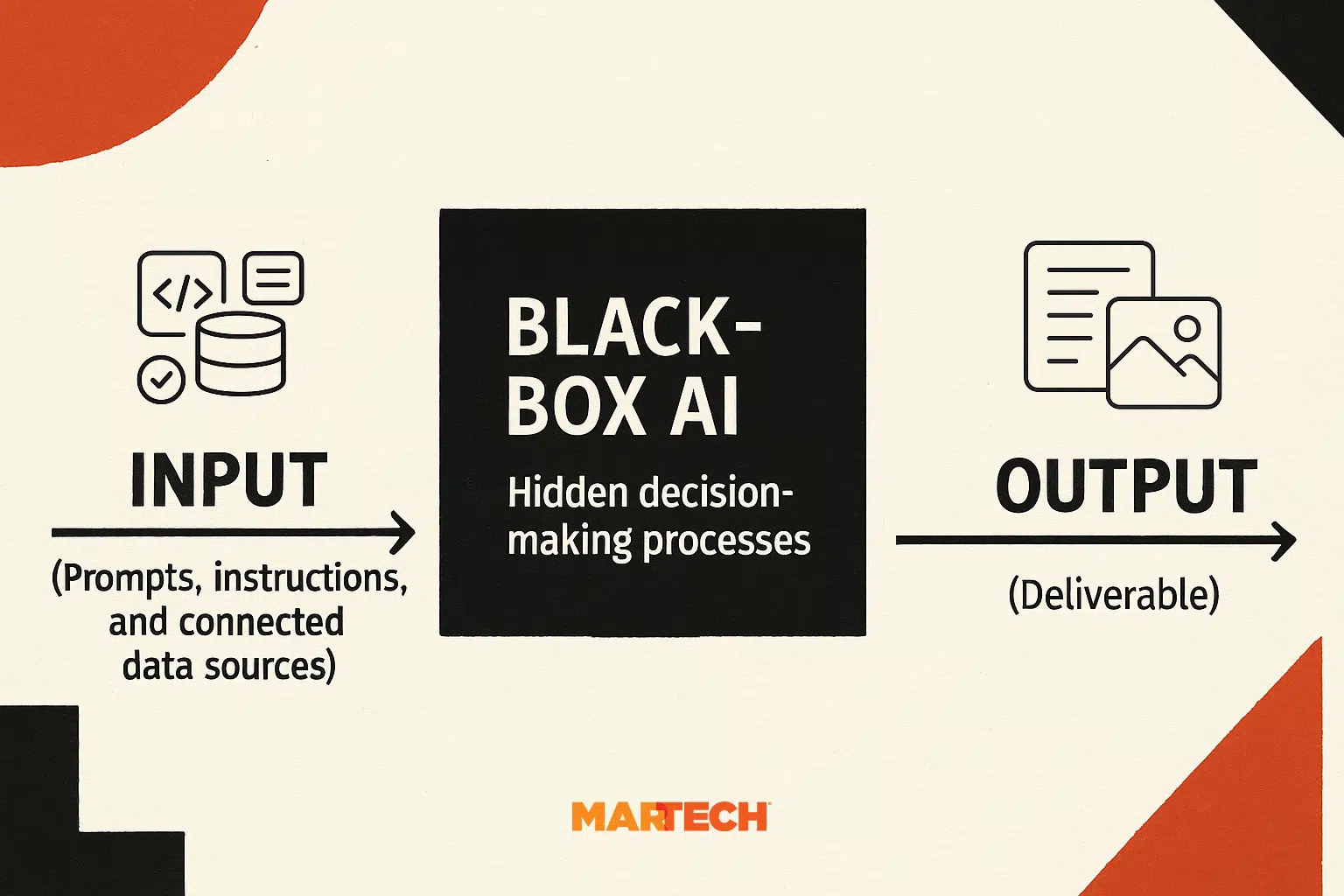
Some organizations may need more transparency so they understand how an AI tool came to certain conclusions. This means they may need to understand, customize, or explain a tool’s decision-making processes.
Note: Large language models (LLMs) and generative AI tools commonly are black-box AI. This is why it’s important to validate their outputs manually.
As a result, you can evaluate the tool’s transparency and control options with the following questions and criteria.
Explainability
Explainability boils down to whether you can understand how the AI reaches its conclusions. This is particularly important for critical decisions like lead scoring, budget allocation, and customer segmentation.
Tools that can’t (or won’t) explain their reasoning make it impossible to validate accuracy or identify bias. This can make it difficult to trust the decision-making process and may introduce potential accuracy and compliance concerns.
Some predictive lead scoring tools, for example, use black-box AI. These tools may give each lead a score, like 85/100, but not elaborate more on why they generated those tools. Sales teams need to know which traits or engagement patterns drove the score so they can tailor their outreach.
Customization
The more you can customize AI tools, the more helpful they can be. It’s important to understand if you can train or fine-tune the AI using your proprietary data and business rules.
Generic AI models may not capture the nuances of your industry, customer base, or business model. This could decrease the quality and relevance of output.
Acrolinx, for example, allows users to fine-tune their LLMs according to your enterprise standards. It will integrate with your existing generative AI workflows to assess, score, and improve content as it’s generated in real-time.
Human oversight
AI will never replace the human touch. You want to determine if an AI tool provides meaningful human-in-the-loop functionality for reviewing and approving AI recommendations.
Fully automated systems can amplify errors at scale, especially when there are no good options for human review and adjustments.
Tools that offer human-in-the-loop features allow your team to step in and guide AI, which can improve output and trust.

Model transparency
Some tools may give you information about the underlying AI models, training data, and algorithmic approaches.
Transparency enables organizations to identify and correct bias before it impacts customers or business outcomes. It can be crucial for compliance, auditing, and long-term strategic planning.
In enterprise environments, transparency and explainability aren’t just nice to have. They may be a requirement for regulatory compliance, risk management, and building stakeholder confidence.
From a risk management perspective, transparency helps you understand potential failure points. If you know what data the model was trained on and how it processes information, you can better predict when it might perform poorly or make mistakes.
Regulatory compliance often requires demonstrating that your decision-making processes are fair and non-discriminatory. Without visibility into how your AI tools work, you can’t prove compliance during audits or investigations.
Getting insight into model transparency—including its algorithmic approaches and what training data is used—can be essential for auditing and risk management.
What governance, privacy, and compliance standards does it meet?
AI solutions can introduce new potential risks around privacy, data security, and compliance that martech buyers should account for.
Have you ever worried about putting proprietary organizational or customer data into a tool like ChatGPT, wondering if it will no longer be proprietary?
Some AI models retain and learn from information, so that data may not be proprietary anymore. This means your competitive advantages, trade secrets, or sensitive customer information could potentially be exposed in the AI’s responses to other users. It may even be used to provide suggestions for your competitors.
AI can also introduce biases into outputs when using tools like content generators or predictive analytics solutions.
With all this in mind, it’s no surprise CoSchedule’s study found that 40.44% of marketers were concerned about data privacy issues and ethical considerations in AI tools.
The following privacy, compliance, and governance considerations should be central in your evaluation process.
Data privacy compliance
It’s important to assess whether an AI platform abides by security and privacy regulations that impact your industry. You also want to make sure a specific platform complies with your own company policies. Some important questions to ask include:
- How does the tool handle sensitive customer data under regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA?
- Does it provide granular controls for data access, retention, and deletion?
- Can it support your privacy policy requirements and customer consent preferences?
For example, Microsoft’s Copilot has strong commercial protections for Microsoft 365 users. The solution keeps your data private and won’t use it to train foundational models. This can help keep proprietary, organizational, and customer data safe.
Platforms that don’t abide by these privacy guidelines could put proprietary or protected data at risk.
For instance, certain customer service chatbots could retain conversation logs containing personal information longer than necessary. This could potentially violate GDPR’s data minimization requirements or could cause the customer interactions with sensitive information to be used in model training.
Bias detection and mitigation
Some AI-powered tools may offer mechanisms to identify and correct algorithmic bias in AI outputs.
This is particularly critical for tools involved in customer segmentation, content personalization, or predictive analytics.
AI could inadvertently discriminate against protected groups based on limited or faulty training data. This risk may increase if there aren’t strong explainability and human oversight options to detect or rectify biases.
Note: Researchers are actively looking for ways to remove bias from AI output. MIT recently developed a new technique that removes select data points from a larger data set until all subgroups were represented equally. This improved performance against underrepresented groups.
For example, Amazon scrapped an AI recruiting tool in 2018 after discovering it systematically downgraded resumes from women. This bias occurred because it was trained primarily on male-dominated hiring data from previous years. The tool penalized resumes that included words like “women’s” (as in “women’s chess club captain”) and favored candidates from all-male colleges.
This kind of bias can expose companies to significant legal liability. Beyond financial costs, biased AI can damage brand reputation, alienate customer segments, and create long-term trust issues that impact revenue.
Audit capabilities
Comprehensive audit trails become essential for compliance reporting, performance analysis, and identifying potential issues before they impact customers. These logs should capture not just what decisions the AI made, but also what data influenced those decisions and when they occurred.
For example, if an AI tool automatically segments customers for marketing campaigns, you need records showing which customers were placed in which segments and what criteria drove those decisions.
This is crucial if you need to explain to regulators why certain groups received different treatment or if customers question why they received specific marketing messages.
Similarly, audit capabilities help you spot performance degradation over time. If your AI lead scoring tool gradually becomes less accurate, detailed logs can help you identify whether the issue stems from data quality problems, model drift, or changes in customer behavior patterns.
Security standards
Your team members will likely share valuable data with AI tools. So, it’s important to understand what cybersecurity measures protect your data.
See if the tool has certifications like SOC 2, ISO 27001, or industry-specific security frameworks relevant to your organization.
Make sure you read each platform’s terms and conditions carefully so you can understand how your input is being used, stored, and accessed. If you have any questions, talk to your organization’s legal and data security experts.
Red flags to watch for may include:
- Vague privacy policies that don’t clearly specify how your data is used, stored, or accessed.
- Vendors that claim ownership rights over your input data or use it to train their models without explicit consent.
- Platforms that store data in unclear locations, lack proper data deletion policies, or can’t provide detailed security infrastructure information.
How does this tool measure and prove Return on Investment (ROI)?
The most sophisticated AI tool is worthless if you can’t measure its business impact. It’s essential to understand how a product could improve specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and what results you can expect.
Note: If the tool can’t prove its value in your marketing funnel, you may want to look elsewhere.
In practice, this means asking vendors for specific metrics like “What percentage improvement in email open rates do similar companies in our industry typically see?” or “How much time does this tool save per campaign compared to manual processes?”
Before implementing any tool, establish clear baseline metrics for your current performance so you can accurately track improvements and calculate ROI over a defined timeframe. ROI measurement should be built into your evaluation criteria from the beginning, and should include the following criteria:
Definition of success metrics
Determining which KPIs signal success with this tool is an important part of tracking performance and ROI.
Key metrics might include conversion rate improvements, cost per acquisition reductions, time savings, or revenue attribution. Be as specific as possible about the KPIs that you plan to track when assessing the ROI of an AI tool.
Establish baseline measurements before implementation so you can accurately measure the tool’s impact, and consider both direct metrics (like increased sales) and indirect benefits (such as improved team productivity).
Additionally, determine how long you’ll need to collect data to see meaningful results. Some AI tools may show immediate improvements while others require months of learning and optimization.
Benchmarking data
Some vendors offer benchmarking or expected lift based on how you plan to use the tool or your organization’s industry.
Benchmarking refers to performance metrics or data points that show how similar organizations in your industry typically perform with the AI tool. This may include average email open rates, conversion improvements, or time savings achieved by companies similar to yours.
Expected lift is the predicted improvement or increase in key performance indicators (like sales, efficiency, or engagement rates) that you can reasonably expect based on your specific use case and implementation of the AI tool.
You don’t want to invest in a platform without a good idea of what results you can expect to see.
Ask vendors for industry benchmarks, case studies with specific performance improvements, and expected timelines for seeing measurable results.
Some companies, like Zapier, publish this information on their websites with testimonials or case studies. Others may have specific data points they can share during a sales call.

Attribution capabilities
Do you know how the tool will track its contribution to marketing outcomes?
Some tools can integrate with your existing attribution models. Others might require separate measurement approaches or third-party tools. Tools with weak attribution capabilities can make ROI demonstration difficult.
Your Attribution Model is Missing 40% of Brand Discovery
✓ Track brand mentions across all AI search platforms in real-time
✓ Connect AI-driven discovery to your existing analytics
✓ Measure sentiment and accuracy of every AI mention
Enterprise-grade AI tracking. Finally.
Reporting and analytics features
Check to see if measurement and reporting capabilities are native to the platform or if they require additional tools and integrations.
The easier it is to track performance, the more likely you are to optimize and expand successful AI implementations.
Make sure that you know what—if any—integrations or add-on services are required to access reporting and analytics features. Add-on services or third-party tools, if needed, come with their own expenses and could be overly-complicated.
Further reading: Choosing AI tools for business impact
Asking the right questions to find the right solution
Don’t let the AI hype and its impressive promises cloud your judgment.
Make decisions based on your current needs, long-term scalability potential, feature alignment, and control options.
It doesn’t matter how great a tool is if it’s redundant, incompatible with your existing tech stack, or a data privacy liability waiting to happen.
Asking the right questions can help you assess a tool’s potential fit. You can also use these tactics to make your buying decision:
- Long-term viability: Does the vendor seem financially stable with a clear product roadmap? AI news evolves rapidly. You want partners who will maintain a competitive edge—not shutter their doors.
- Customer feedback and case studies: What do existing customers say about implementation challenges, ongoing support, and results? Look for detailed case studies from companies similar to yours.
- Consider potential challenges: Will the new tool make existing processes slightly more complicated? Could it introduce new layers of risk? Consider potential challenges alongside ROI.
When in doubt, talk to your team. They can weigh in on critical pain points, process bottlenecks, and concerns about specific AI tech. Their input can help you feel more confident in your buying decisions.
Want to learn more about how to leverage generative AI for your company? Download our Marketer’s Guide to Generative AI for Content Creation to for profiles of 11 generative AI vendors that include pricing and capability comparisons.
And stay up-to-date with the latest news in AI development, including latest trends, use cases, and tactics with AI marketing news from MarTech.
New on MarTech